SS7 for the
Common Man
Last modified: Sat, 01 Nov 2008 14:12:38 GMT
| Home |
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
| ||
WAN Documentation
Description: OpenSS7 Project Library Transport WAN
A PDF version of this document is available here.
Wide Area Network Interface
Wide Area Network Interface
1 Introduction
The Wide Area Network (WAN) Interface was developed by Spider Systems, Ltd., (now a division of Emerson Power) and is widely available on many platforms. For example, AIX AIXlink/X.25, HP-UX HP X.25/9000, Solaris Solstice X.25 and SunLink X.25, IRIX IRIS SX.25, PT X.25, RadiSys WAN and SBE X.25 implement the Wide Area Newtork (WAN) Interface.
The Wide Area Network (WAN) Inteface was designed to be used directly with standard STREAMS system calls and does not require the use of a cooperating user space shared library. Applications program directly use the getmsg(2s), getpmsg(2), putmsg(2s) and putpmsg(2) system calls.1 Nevertheless, user shared object libraries can easily be constructed using this STREAMS service primitive interface.
The system header files that must be included when compiling user applications, or STREAMS drivers and modules that use the interface, are detailed in WAN Header Files.
A user library, libcdiapi, is provided, not for interfacing to the message primitive service interface, but for providing various helper functions when using the STREAMS service interface. This library is detailed in WAN Library.
2 Model of the WAN Layer
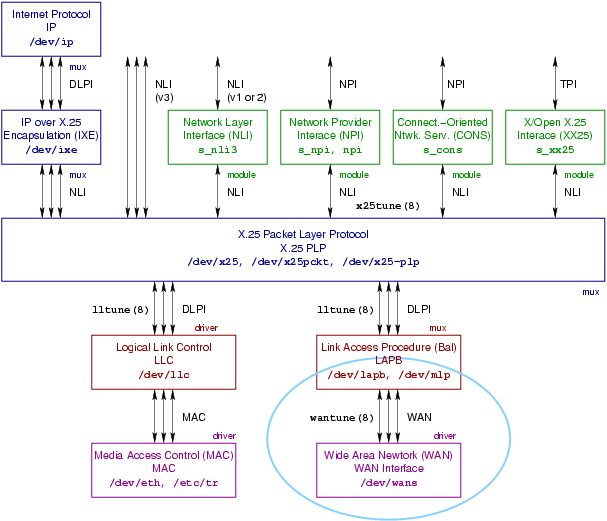
3 WAN Services
3.1 WAN Commands
3.2 WAN Data Structures
4 WAN Message Primitives
The /usr/include/strx25/sys/snet/wan_proto.h header file (<sys/snet/wan_proto.h> with proper compile flags) contains definitions and declarations of primitive structures and field values.
The WAN_primitives union is formatted as follows:
union WAN_primitives {
uint8_t wan_type;
struct wan_sid wsid;
struct wan_reg wreg;
struct wan_ctl wctl;
struct wan_msg wmsg;
struct wan_nty wnty;
};
The WAN_primitives union contains the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. Always one of the following values:WAN_SIDThe contained structure is a wan_sidstructure.WAN_REGThe contained structure is a wan_regstructure.WAN_CTLThe contained structure is a wan_ctlstructure.WAN_DATThe contained structure is a wan_msgstructure.WAN_NTYThe contained structure is a wan_ntystructure. wsid- The structure of the primitive when
wan_typeisWAN_SID. wreg- The structure of the primitive when
wan_typeisWAN_REG. wctl- The structure of the primitive when
wan_typeisWAN_CTL.See WAN_CTL - Control.
wmsg- The structure of the primitive when
wan_typeisWAN_DAT.See WAN_DAT - Data.
wnty- The structure of the primitive when
wan_typeisWAN_NTY.See WAN_NTY - Notify.
These primitive types are described in detail in the sections that follow.
4.1 WAN_SID - Set Subnetwork Identifier
Requests that the WAN driver assign the specified subnetwork identifier to the
Stream and associate the Stream with the underlying device identified by the
subnetwork identifier. This primitive is equivalent to the
CD_ATTACH_REQ(7) primitive of the cdi(7).
Format
The primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block containing a
wan_sid structure.
The wan_sid structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_sid {
uint8_t wan_type;
uint8_t wan_spare[3];
uint32_t wan_snid;
};
Parameters
The wan_sid structure contains the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. AlwaysWAN_SID. wan_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: ignored by the responder and set to zero by the
initiator.
wan_snid- Conveys the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the Physical Point of Attachment (PPA) of the WAN interface.
Response
Should an error occur, an M_ERROR message is sent upstream with an
appropriate error code, resulting in the failure of all system calls on the
Stream until closed. The WAN_SID primitive may fail when:
ENODEV- The specified
wan_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The
M_PROTOmessage block is of an incorrect length for the primitive. EEXIST- The
wan_snidspecified is in use by another Stream. ERANGE- The
wan_snidmember contains invalid information. EBUSY- The physical channel referenced by the
wan_snidis in use by another Stream. ENOSR- The s_wan module, or underlying CDI driver lacks the STREAMS
resources necessary to satisfy the request.
EIO- The
WAN_SIDprimitive was issued from an incorrect state for the subnetwork entity. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
4.2 WAN_REG - Register Subnetwork Identifier
Registers the subnetwork identifier specified in the wan_snid field of
the primitive. Once a subnetwork entity has been registered, it cannot be tuned
or otherwise altered unless disabled with
W_DISABLE.2 This primitive is used by management applications to place
subnetwork entities into service.
Format
The primitive consists of one M_PROTO message block containing a
wan_reg structure.
The wan_reg structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_reg {
uint8_t wan_type;
uint8_t wan_spare[3];
uint32_t wan_snid;
};
Parameters
The wan_reg structure contains the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. AlwaysWAN_REG. wan_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: ignored by the responder and set to zero by the
initiator.
wan_snid- Conveys the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the Physical Point of Attachment (PPA) of the WAN interface.
Response
Should an error occur, an M_ERROR message is sent upstream with an
appropriate error code, resulting in the failure of all system calls on the
Stream until closed. The WAN_REG primitive may fail when:
ENODEV- The specified
wan_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The
M_PROTOmessage block is of an incorrect length for the primitive. EXDEV- There exists a hardware configuration error for the specified
wan_snid. EBUSY- The physical channel referenced by the
wan_snidis in use by another Stream. EIO- The
WAN_REGprimitive was issued from an incorrect state for the subnetwork entity. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
ENOMEM- There was insufficient memory immediately available to register the subnetwork
identity.
E2BIG- The maximum receive buffer size is too small to hold the largest frame required by the device.
4.3 WAN_CTL - Control
This primitive class consists of four primitives used to enable or disable the
WAN interface. These primitives are equivalent to the
CD_ENABLE_REQ(7), CD_ENABLE_CON(7),
CD_DISABLE_REQ(7), CD_DISABLE_CON(7), and the
CD_ERROR_IND(7) primitives of the cdi(7).
Format
The WAN_CTL primitives consist of one M_PROTO message block
containing a wan_ctl structure.
The wan_ctl structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_ctl {
uint8_t wan_type;
uint8_t wan_command;
uint8_t wan_remtype;
uint8_t wan_remsize;
uint8_t wan_remaddr[20];
uint8_t wan_status;
uint8_t wan_diag;
};
Usage
The WC_CONNECT command is valid from the WAN user to the WAN driver; or
from the WAN driver to the WAN user.
Fields wan_remtype, wan_remsize and wan_remaddr are
significant, wan_status and wan_diag are ignored.
This WC_CONCNF command is valid when sent from the WAN driver to the WAN
user; or from the WAN user to the WAN driver.
Fields wan_status and wan_diag are significant,
wan_remtype, wan_remsize and wan_remaddr are ignored.
This WC_DISC command is valid when sent from the WAN user to the WAN
driver; or from the WAN driver to the WAN user.
All fields are ignored.
This WC_DISCCNF command is valid when sent from the WAN driver to the WAN
user; or from the WAN user to the WAN driver.
Fields wan_status and wan_diag are significant,
wan_remtype, wan_remsize and wan_remaddr are ignored.
Parameters
The wan_ctl structure contains the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. AlwaysWAN_CTL. wan_command- Conveys the WAN command. This field may assume one of the following values:
WC_CONNECTThe primitive is a connect request or indication. WC_CONCNFThe primitive is a connect confirmation. WC_DISCThe primitive is a disconnect request of indication. WC_DISCCNFThe primitive is a disconnect confirmation. wan_remtype- When significant, conveys the type of the remote address. This field may have
one of the following values:
WAN_TYPE_ASC- The
wan_remaddrfield contains ASCII coded digits. Thewan_remsizefield contains the number of digits (in octets). WAN_TYPE_BCD- The
wan_remaddrfield contains BCD encoded digits. Thewan_remsizefield contains the number of digits (in semi-octets).
This field is only significant in the
WC_CONNECTprimitive, and for devices that have call procedural definitions. Otherwise, the field is set to zero (0). wan_remsize- When significant, conveys the length of the remote address in digits (either
octets or semi-octets depending on the
wan_remtypemember).This field is only significant in the
WC_CONNECTprimitive, and for devices that have call procedural definitions. Otherwise, the field is set to zero (0). wan_remaddr- When significant, conveys the remote address. The address contianed in this
field is either represented as ASCII digits or BCD encoded digits, depending on
the value of the
wan_remtypefield. This field is only significant in theWC_CONNECTprimitive.This field is only significant in the
WC_CONNECTprimitive, and for devices that have call procedural definitions. Otherwise, the field is set to null. wan_status- When significant, provides the status for the
WC_CONCNForWC_DISCCNFcommand. This field can assume one of the following values:WAN_FAIL- The preceding
WC_CONNECTorWC_DISCcommand was unsuccessful. The link remains in the disconnected or connected state as the case may be. WAN_SUCCESS- The preceding
WC_CONNECTorWC_DISCcommand was successful. The link moves to the connected or disconnected state as the case may be.
This field is only significant in the
WC_CONCNFandWC_DISCprimitives. wan_diag- When significant and the status field is
WAN_FAIL, provides diagnostic information concerning the failure. This field is only significant in theWC_CONCNFandWC_DISCCNFprimitives when failure is indicated.
State
The WC_DISCCNF command is only valid in response to a preceding and
corresponding WC_DISC command from the opposite direction.
The WC_DISC and WC_DISCCNF commands are valid during the
connecting, data transfer, or disconnecting phases.
The WC_CONCNF command is only valid in response to a preceding and
corresponding WC_CONNECT command from the opposite direction.
The WC_CONNECT and WC_CONCNF commands are valid during the
idle or connecting phases.
Response
Should an error occur, an M_PROTO message is sent upstream with an
appropriate error code, resulting in the failure of all system acalls on the
Stream until closed. The WAN_CTL primitive may fail when:
EINVAL- The
M_PROTOmessage block is of an incorrect length for the primitive, or thewan_commandis invalid. ENXIO- The underlying device driver has encountered a fatal error.
EIO- The
WAN_CTLprimitive was issued form an incorrect state for the subnetwork entity. E2BIG- The maximum receive buffer size is too small to hold the largest frame required by the device.
Equivalence
When sent from the WAN user, the WC_CONNECT command corresponds to the
CD_ENABLE_REQ(7) primitive of the cdi(7).
When sent from the WAN driver, the primitive has no corresponding primitive.
When from the WAN driver, WC_CONCNF corresponds to
CD_ENABLE_CON(7).
When from the WAN user, WC_CONCNF has no corresponding primitive.
When to the WAN driver, WC_DISC
corresponds to CD_DISABLE_REQ(7).
When from the WAN driver to the WAN user, WC_DISC corresponds to
CD_ERROR_IND(7).
When from the WAN driver, WC_DISCCNF
corresponds to CD_DISABLE_CON(7).
When to the WAN driver, WC_DISCCNF has no
corresponding primitive.
Compatibility
Some implementations ignore all of the parameter fields of the wan_ctl
structure other than wan_type and wan_command, as is normally
the case for WAN_NONE: no call procedural definitions.
4.4 WAN_DAT - Data
This primitive class provides two primitives for the transfer of data across the
service interface. Attached M_DATA message blocks contain user data.
Format
The WAN_DAT primitive contains a wan_msg structure. The primitive
consists of one M_PROTO message block followed by one or more M_DATA
message blocks containing user data.
The M_PROTO message block is structured as follows:
struct wan_msg {
uint8_t wan_type;
uint8_t wan_command;
};
Usage
The WC_TX command specifies that the user data in the associated
M_DATA message blocks consist of data for transmission.
The WC_RX command indicates that the user data in the associated
M_DATA message blocks consist of received data.
Parameters
The wan_msg structure contains the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. AlwaysWAN_DAT. wan_command- Conveys the WAN command. This field may assume one of the following values:
WC_TX- Specifies that the user data in the associated
M_DATAmessage blocks consist of data for transmission. WC_RX- Indicates that the user data in the associated
M_DATAmessage blocks consist of received data.
State
The WAN_DAT primitive may be issued by WAN user or WAN driver in the data
transfer phase.
Response
Should an error condition occur, an M_ERROR message is sent upstream with
an appropriate error code, resulting in the failure of all system calls on the
Stream until closed. The WAN_DAT primitive may fail when:
EINVAL- The
M_PROTOmessage block is of an incorrect length for the primitive. ENXIO- The underlying device driver has encountered a fatal error.
EIO- The
WAN_DATprimitive was issued from an incorrect state for the subnetwork entity. E2BIG- The maximum receive buffer size is too small to hold the largest frame required by the device.
Equivalence
These primitives are equivalent to the CD_UNITDATA_REQ(7) and
CD_UNITDATA_IND(7) primitives of the cdi(7).
The WC_TX primitive, issued by the WAN user, is equivalent to the
CD_UNITDATA_REQ(7) primitive;
the WC_RX, issued by the WAN driver, the
CD_UNITDATA_IND(7).
Compatibility
Some implementations provide additional wan_command values with
hardware- or implementation-specific fields. Some implementations also define a
structure for the initial portion of the M_DATA block that contains media-
or hardware-specific fields.
4.5 WAN_NTY - Notify
Registers for or provide notification of events for the wan_snid field
of the primitive. When passed to the WAN driver, the primitive requests that
the WAN driver record the events for which notification is to be given. When
passed to the WAN user, the primitive notifies of a triggered event.
This primitive corresponds to the CD_MODEM_SIG_IND(7) and
CD_ERROR_IND(7) primitives of the cdi(7).
Format
The primitive consists of a signle M_PROTO message block containing a
wan_nty structure.
The wan_nty structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_nty {
uint8_t wan_type;
uint8_t wan_spare[3];
uint32_t wan_snid;
uint32_t wan_eventstat;
uint32_t wan_reserved[2];
};
Parameters
The wan_nty structure has the following members:
wan_type- Specifies the type of the structure contained in the
M_PROTOmessage block. AlwaysWAN_NTY. wan_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: ignored by the responder and set to zero by the
initiator.
wan_snid- Conveys the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA) of the WAN interface.
wan_eventstat- This member contains one of the following bit masks:
W_RECEIVE_BUFFER_OVFLA received buffer overflow has occurred. W_FRAMING_ERRORA received frame framing error has occured. W_TIMEOUTA timeout has occurred. W_HD_OVERRUNA hardware device overrun has occurred. W_ATTACHED_DEV_INACTThe attached device has gone inactive. W_ATTACHED_DEV_ACTIVEThe attached device has become active. W_FCS_ERRA Frame Check Sequence (CRC) error has occurred. W_CTS_ONThe CTS (Clear to Send) lead has gone high. W_CTS_OFFThe CTS (Clear to Send) lead has gone low. W_DCD_ONThe DCD (Data Carrier Detect) lead has gone high. W_DCD_OFFThe DCD (Data Carrier Detect) lead has gone low. W_DSR_ONThe DSR (Data Set Ready) lead has gone high. W_DSR_OFFThe DSR (Data Set Ready) lead has gone low. W_RI_ONThe RI (Ring Indicator) lead has gone high. W_RI_OFFThe RI (Ring Indicator) lead has gone low. W_PARITY_ERRORA parity error has occurred on an asynchronous line. W_BREAK_DETECTEDA break has been detected on an asyncrhonous line. W_SHORT_FRAMEA short frame has been received. W_TX_UNDERRUNThe transmitter FIFO has underrun. W_ABORTAn aborted frame has been received. W_RCL_NONZEROW_BSC_PAD_ERRA Bisynchronous Character padding error has occured. W_CTS_UNDERRUNA Clear to Send underrun condition has occurred. wan_reserved- Reserved for future use: set to zero by the issuer and ignored by the receiver.
State
The WAN_NTY primitive may be issued by WAN user or WAN driver in the
connecting, data transfer, disconnecting, and disconnected phases.
Response
When WAN_NTY is issued by the WAN driver, the WAN driver does not expect
any response.
When issued by the WAN interface user, the WAN interface user expects the WAN
driver to register the specified events and generate a WAN_NTY primitive
should any of the registered events be detected, and to not generate a
WAN_NTY primitive for any events that have not been registered.
Should an error occur as a result of a primitive issued by the WAN interface
user, an M_PROTO message is sent upstream with an appropriate error code,
resulting in the failure of all system acalls on the Stream until closed. The
WAN_NTY primitive may fail when:
EINVAL- The
M_PROTOmessage block is of an incorrect length for the primitive, or thewan_commandis invalid. ENXIO- The underlying device driver has encountered a fatal error.
EIO- The
WAN_CTLprimitive was issued form an incorrect state for the subnetwork entity. E2BIG- The maximum receive buffer size is too small to hold the largest frame required by the device.
Equivalence
When issued by the WAN user, the WAN_NTY primitive is equivalent to the
CD_MODEM_SIG_POLL(7) primitive of the cdi(7).
When issued by the WAN driver, the WAN_NTY primitive is equivalent to the
CD_MODEM_SIG_IND(7) and CD_ERROR_IND(7) primitive.
Compatibility
The WAN_NTY primitive is OpenSS7-specific and was modelled after
the IBM WAN_NOTIFY primitive included in the ARTIC
implementation.3 While WAN_NTY is
similar in structure and form to WAN_NOTIFY when issued by the WAN
driver, WAN_NTY also permits registration of events when issued by the
WAN interface user. This is accomplished in ARTIC using the
W_SETLINE and W_GETLINE and other device-dependent input-output
controls.
The default behaviour for a freshly created Stream is to not generate any
notifications at all. This provides maximum compatibility with implementations
for which applications programs, drivers and modules are not expecting to
receive WAN_NTY or WAN_NOTIFY primitives.
5 WAN Input-Output Controls
5.1 Input-Output Control Data Structures
The /usr/include/strx25/sys/snet/wan_control.h header file (<sys/snet/wan_control.h> with proper compile flags) defines a number of structures, pointers to which are used as arguments to input-output controls. These structures fall into four classes, identified by the value of the first byte of the structure, as follows:
WAN_STATS | A wan_stioc structure that identifies the
subnetwork and contains the state and statistics associated with the subnetwork.
Used with the W_ZEROSTATS and W_GETSTATS input-output controls.
|
WAN_TUNE | A wan_tnioc structure that idnetifies the
subnetwork and contains the tunable parameters associated with the subnetwork.
Used with the W_SETTUNE and W_GETTUNE input-output controls.
|
WAN_MAP | A wanmapgf, wanmappf or wanmapdf
structure that identifies the mapping entries, mapping entry or subnetwork,
respectively. Used with the W_GETWANMAP, W_PUTWANMAP and
W_DELWANMAP input-output controls, respectively.
|
WAN_PLAIN | A wan_hdioc structure that identifies the
subnetwork. Used with the W_STATUS, W_ENABLE and W_DISABLE
input-output controls.
|
WAN_SETSIG | A wan_setsigf structure that identifies the
subnetwork and contains the setting for leads associated with the subnetwork.
Used with the W_SETSIG and W_GETSIG
input-output controls.
|
These structures are described in detail in the subsections that follow.
5.1.1 WAN_STATS - Statistics Data Structures
The value of WAN_STATS in the w_type field of the structure
pointed to by the input-output control argument specifies that the pointed-to
structure is a wan_stioc structure. This structure is used by the
W_ZEROSTATS and W_GETSTATS input-output controls.
5.1.1.1 wan_stioc Structure
The wan_stioc structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_stioc {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_state;
uint8_t w_spare[2];
uint32_t w_snid;
hdlcstats_t hdlc_stats;
};
The wan_stioc structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_STATS. w_state- Returns the state of the subnetwork entity. This member may have one of the
following values:
HDLC_IDLEThe raw HDLC connection is idle. HDLC_ESTBThe raw HDLC connection is established. HDLC_DISABLEDThe raw HDLC connection is disabled. HDLC_CONNThe raw HDLC connection is connecting. HDLC_DISCThe raw HDLC connection is disconnecting. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA).
hdlc_stats- Contains the
hdlcstats_tstructure described below.
5.1.1.2 hdlcstats_t Structure
The hdlcstats_t structure is formatted as follows:
typedef struct hstats {
uint32_t hc_txgood;
uint32_t hc_txurun;
uint32_t hc_rxgood;
uint32_t hc_rxorun;
uint32_t hc_rxcrc;
uint32_t hc_rxnobuf;
uint32_t hc_rxnflow;
uint32_t hc_rxoflow;
uint32_t hc_rxabort;
uint32_t hc_intframes;
} hdlcstats_t;
The hdlcstats_t structure has the following members, each reflecting a
count since the last reset:
hc_txgood- A count of the number of good frames transmitted since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_txurun- A count of the number of transmitter underruns since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxgood- A count of the number of good frames received since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxorun- A count of the number of receiver overruns since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxcrc- A count of the number of received CRC or framing errors since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxnobuf- A count of the number of receive buffer overflows since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxnflow- A count of the number of received frames with no flow control since the last
reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxoflow- A count of the number of received buffer overflows since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_rxabort- A count of the number of receiver aborts since the last reset.
This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it
will no longer be incremented.
hc_intframes- A count of the number of frames failed to be transmitted by the loss of modem signals or other physical medium error since the last reset. This is a non-wrapping counter: should the counter reach its maximum value, it will no longer be incremented.
5.1.2 WAN_TUNE - Tunable Data Structures
The value of WAN_TUNE in the w_type field of the structure
pointed to by the input-output control argument specifies that the pointed-to
structure is a wan_tnioc structure. This structure is used by the
W_SETTUNE and W_GETTUNE input-output controls.
5.1.2.1 wan_tnioc Structure
The wan_tnioc structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_tnioc {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
wantune_t wan_tune;
};
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_TUNE. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA).
wan_tune- Contains the
wantune_tstructure described below.
5.1.2.2 wantune_t Structure
The wantune_t structure is formatted as follows:
typedef struct {
uint16_t WAN_options;
struct WAN_hddef WAN_hd;
} wantune_t;
The wantune_t structure contains the following members:
WAN_options- Specifies a number of WAN options associated with the device. This member is a
bitwise OR of zero or more of the following values:
TRANSLATE- When set, indicates that a translation using the WAN remote address to interface address mapping function is to be performed.
WAN_pad- Padding for alignment, set to zero by the issuer and ignored by the responder.
WAN_hd- Contains the
WAN_hddefstructure described below.
5.1.2.3 WAN_hddef Structure
The WAN_hddef structure is formatted as follows:
struct WAN_hddef {
uint16_t WAN_maxframe;
uint32_t WAN_baud;
uint16_t WAN_interface;
union {
uint16_t WAN_cptype;
struct WAN_x21 WAN_x21def;
struct WAN_v25 WAN_v25def;
} WAN_cpdef;
};
The WAN_hddef structure contains the following members:
WAN_maxframe- Conveys the maximum frame size in octets.
WAN_baud- Conveys the transmission rate in bits per second.
WAN_interface- This member specifies the WAN interface. It can assume one of the following
values:
WAN_X21The interface is a X.21 interface. WAN_V28The interface is a V.28 interface. WAN_V35The interface is a V.35 interface. WAN_V36The interface is a V.36 interface. WAN_RS232The interface is a RS-232 interface. WAN_RS422The interface is a RS-422 interface. WAN_T1E1The interface is a G.703/G.704 interface. WAN_ATMThe interface is a ATM interface. WAN_cpdef- This member defines a number of alternate call procedural defintions described
by a union. The union contains the following members:
WAN_cptype- Specifies the tye of the call procedural definitions. Always
WAN_NONE,WAN_X21PorWAN_V25bis. WhenWAN_cptypeisWAN_NONE, only this member of the union is significant. WAN_x21def- When
WAN_cptypeisWAN_X21P, this member of the union is significant. This member contains theWAN_x21structure described below. WAN_v25def- When
WAN_cptypeisWAN_V25bis, this member of the union is significant. This member contains theWAN_v25structure described below.
5.1.2.4 WAN_x21 Structure
The WAN_x21 structure is formatted as follows:
struct WAN_x21 {
uint16_t WAN_cptype;
uint16_t T1;
uint16_t T2;
uint16_t T3A;
uint16_t T4B;
uint16_t T5;
uint16_t T6;
};
The WAN_x21 structure has the following members:
WAN_cptype- Specifies the type of the call procedural defintions. Always
WAN_X21P. T1- Specifies the timeout for the call request state in deciseconds.
T2- Specifies the timeout for the EOS to data transfer in deciseconds.
T3A- Specifies the timeout for call progress signals in deciseconds.
T4B- Specifies the timeout for DCE provided information in deciseconds.
T5- Specifies the timeout for DTE clear request in deciseconds.
T6- Specifies the timeout for DTE clear confirm state in deciseconds.
5.1.2.5 WAN_v25 Structure
The WAN_v25 structure is formatted as follows:
struct WAN_v25 {
uint16_t WAN_cptype;
uint16_t callreq;
};
The WAN_v25 structure has the following members:
WAN_cptype- Specifies the type of the call procedural defintions. Always
WAN_V25bis. callreq- Contains the abort time (in deciseconds) for the call request command if the network does not support CFI.
5.1.3 WAN_MAP - Mapping Data Structures
The value of WAN_MAP in the w_type field of the structure
pointed to by the input-output control argument specifies that the pointed-to
structure is a wanmapgf, wanmappf or wanmapdf structure.
These structures are used by the W_GETWANMAP, W_PUTWANMAP and
W_DELWANMAP input-output controls, respectively.
5.1.3.1 wanmapgf Structure
The wanmapgf structure is formatted as follows:
struct wanmapgf {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
wanget_t wan_ents;
};
The wanmapgf structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_MAP. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA).
wan_ents- Contains the
wanget_tstructure described below.
5.1.3.2 wanget_t Structure
The wanget_t structure is formatted as follows:
typedef struct {
uint16_t first_ent;
uint16_t num_ent;
wanmap_t entries[0];
} wanget_t;
The wanget_t structure contains the following members:
first_ent- Specifies the index of the first entry in the
entriesmember. num_ent- Specifies the number of entries in the
entriesmember. entries- Contains
num_ententries ofwanmap_tstructures. Thewanmap_tstructure is described below.
5.1.3.3 wanmappf Structure
The wanmappf structure is formatted as follows:
struct wanmappf {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
wanmap_t wan_ent;
};
The wanmappf structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_MAP. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA).
wan_ent- Contains the
wanmap_tstructure described below.
5.1.3.4 wanmap_t Structure
The wanmap_t structure is formatted as follows:
typedef struct {
uint8_t remsize;
uint8_t remaddr[20];
uint8_t infsize;
uint8_t infaddr[30];
} wanmap_t;
The wanmap_t structure contains the following members:
remsize- Conveys the size of the remote address contained in the
remaddrfield in octets. remaddr- Contains the remote address, significant to
remsizeoctets. infsize- Conveys the size of the interface address contained in the
infaddrfield in octets. infaddr- Contains the remote address, significant to
infsizeoctets.
5.1.3.5 wanmapdf Structure
The wanmapdf structure is formatted as follows:
struct wanmapdf {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
};
The wanmapdf structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_MAP. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of Attachment (PPA).
5.1.4 WAN_PLAIN - Plain Data Structures
The value of WAN_PLAIN in the w_type field of the structure
pointed to by the input-output control argument specifies that the pointed-to
structure is a wan_hdioc structure. The structure is used by the
W_STATUS, W_ENABLE and W_DISABLE input-output controls.
5.1.4.1 wan_hdioc Structure
The wan_hdioc structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_hdioc {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
};
The wan_hdioc structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_PLAIN. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of Attachment (PPA).
5.1.5 WAN_SETSIG - Signal and Lead Data Structures
The value WAN_SETSIG in the w_type field of the structure
pointed to by the input-output control argument specifies that the pointed-to
structure is a wan_setsigf structure. This structure is used by the
W_SETSIG and W_GETSIG input-output controls.
5.1.5.1 wan_setsigf Structure
The wan_setsigf structure is formatted as follows:
struct wan_setsigf {
uint8_t w_type;
uint8_t w_spare[3];
uint32_t w_snid;
wan_setsig_t wan_setsig;
};
The wan_setsigf structure contains the following members:
w_type- Specifies the type of the structure associated with the input-output control.
Always
WAN_SETSIG. w_spare- Spare bytes for alignment: set to zero (0) by the issuer and ignored by the
responder.
w_snid- Specifies the subnetwork identifier. Equivalent to the CDI Physical Point of
Attachment (PPA).
wan_setsig- Contains the
wan_setsig_tstructure described below.
5.1.5.2 wan_setsig_t Structure
The wan_setsig_t structure is formatted as follows:
typedef struct {
uint8_t w_ctrlsignal;
uint8_t w_reserved[3];
} wan_setsig_t;
The wan_setsig_t structure contains the following members:
w_ctrlsignal- Contains the control signals. This can be a bitwise OR of zero or more of the
following:
W_RTS_HIGHSet or indicate RTS high, (or X.21 C signal). W_DTR_HIGHSet or indicate DTR high. W_DCD_HIGHIndicate DCD high. W_DSR_HIGHIndicate DSR high. W_CTS_HIGHIndicate CTS high, (or X.21 I signal). W_RI_HIGHIndicate RI high. W_RTS_LOWSet RTS low. W_DTR_LOWSet DTR low. w_reserved- Reserved field: set to zero (0) by issuer and ignored by responder.
5.2 Input-Output Control Commands
The /usr/include/strx25/sys/snet/wan_control.h header file (<sys/snet/wan_control.h> with proper compile flags) defines a number of input-output controls, as follows:
W_ZEROSTATS | Zeroes statistics associated with a subnetwork entity and collects the statistics and
state of the subnetwork prior to reset.
|
W_GETSTATS | Retrieves the statistics and state associated with a subnetwork entity.
|
W_SETTUNE | Sets the tunable parameters associated with a subnetwork entity.
|
W_GETTUNE | Gets the tunable parameters associated with a subnetwork entity.
|
W_PUTWANMAP | Puts a remote address to interface address mapping entry.
|
W_GETWANMAP | Gets a block of remote address to interface address mapping entries.
|
W_DELWANMAP | Deletes all remote address to interface address mapping entries associated with a
subnetwork entity.
|
W_STATUS | Retrieves the state of a subnetwork entity.
|
W_ENABLE | Enables a subnetwork entity for data transfer.
|
W_DISABLE | Disables a subnetwork entity from data transfer.
|
These input-output controls are described in detail in the subsections that follow.
5.2.1 W_ZEROSTATS - Zero Statistics
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_stioc structure, see wan_stioc Structure.
Description
The W_ZEROSTATS input-output control requests that the WAN driver reset
the statistics associated with the w_snid contained in the passed-in
structure.
The WAN driver is to reset the statistics, returning the statistics and state
immediately before reset in the hdlc_stats and w_state members
of the provided structure.
See hdlcstats_t Structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.2 W_GETSTATS - Get Statistics
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_stioc structure, see wan_stioc Structure.
Description
The W_GETSTATS input-output control requests that the WAN driver retrieve
the statistics and state associated with the w_snid contained in the
passed-in structure.
The WAN driver is to retrieve the current statistics and state, returning them
in the hdlc_stats and w_state members of the provided
structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.3 W_SETTUNE - Set Tunables
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_tnioc structure, see wan_tnioc Structure.
Description
The W_SETTUNE input-output control requests that the WAN driver set the
tunable parameters form the passed-in structure for the w_snid
contained in that structure.
The WAN driver is to set th tunable, returning any negotiated value in the
provided structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
E2BIG- The specified
WAN_maxframeis of insufficient size to hold the maximum size frame necessary for proper operation of the protocol. ENOMEM- The WAN driver cannot allocate single message buffers of size
WAN_maxframe. EIO- The interface is in a wrong state. For example, the tuning input-output control
was issued after the interface was already registered with the
WAN_REGprimitive. EXDEV- The
WAN_interfacedoes not match the capabilities or mode of the hardware.
Compatibility
5.2.4 W_GETTUNE - Get Tunables
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_tnioc structure, see wan_tnioc Structure.
Description
The W_GETTUNE input-output control requests that the WAN driver get the
tunable parameters associated with the w_snid contained in the
passed-in structure.
The WAN driver is to retrieve the tunable parameters and return them in the
provided structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.5 W_PUTWANMAP - Put WAN Address Mapping
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wanmappf structure, see wanmappf Structure.
Description
The W_PUTWANMAP input-output control requests that the WAN driver add a
remote address to interface address mapping entry associated to the specified
subnetwork identifier, w_snid.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.6 W_GETWANMAP - Get WAN Address Mapping
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wanmapgf structure, see wanmapgf Structure.
Description
The W_GETWANMAP input-output control requests that the WAN driver
retrieve a block of remote address to interface address mapping entries
associated with the specified subnetwork identifier, w_snid.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.7 W_DELWANMAP - Delete WAN Address Mappings
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wanmapdf structure, see wanmapdf Structure.
Description
The W_DELWANMAP input-output control requests that the WAN driver delete
all remote address to interface address mapping entries associatedw with the
specified subnetwork identifier, w_snid.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.8 W_STATUS - Get Interface Status
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_hdioc structure, see wan_hdioc Structure.
Description
The W_STATUS input-output control requests that the WAN driver return the
status of the w_snid contained in the passed-in structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0) when the
associated w_snid is disabled, and one (1) when the associated
w_snid is enabled.
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.9 W_ENABLE - Enable Interface Data Transfer
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_hdioc structure, see wan_hdioc Structure.
Description
The W_ENABLE input-output control requests that the WAN driver enable
data transfer for the w_snid contained in the passed-in structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.10 W_DISABLE - Disable Interface Data Transfer
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_hdioc structure, see wan_hdioc Structure.
Description
The W_DISABLE input-output control requests that the WAN driver disable
data transfer for the w_snid contained in the passed-in structure.
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.11 W_SETSIG - Set Signals and Leads
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_setsigf structure, see wan_setsigf Structure.
Description
The W_SETSIG input-output control requests that the WAN driver set the
signals and leads as specified.
This input-output control is equivalent to the CD_MODEM_SIG_REQ(7)
primitive of the cdi(7).
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
5.2.12 W_GETSIG - Get Signals and Leads
Argument
This input-output control takes an argument that is a pointer to a
wan_setsigf structure, see wan_setsigf Structure.
Description
The W_GETSIG input-output control requests that the WAN driver retrieve
the signals and leads.
This input-output control is equivalent to the CD_MODEM_SIG_POLL(7)
primitive of the cdi(7).
Return Value
When successful, the input-output control operation returns zero (0).
In addition to the errors that may be returned by ioctl(2) and
streamio(7), errors that may be returned by this input-output control
are as follows:
ENODEV- The specified
w_snidis unknown or invalid. EINVAL- The size of the structure corresponding to the passed-in argument is incorrect
for the input-output control and
w_typespecified. ENXIO- The underlying device has encountered a fatal error.
Compatibility
Appendix A WAN Header Files
Applications using the Wide Area Network (WAN) Interface need to include several system header files:
- <errno.h>
- <sys/types.h>
- <sys/ioctl.h>
- <sys/stropts.h>
- <sys/snet/wan_proto.h>
- <sys/snet/wan_control.h>
- <sys/types.h>
A.1 WAN Protocol Header File
A.2 WAN Control Header File
Appendix B WAN Drivers and Modules

B.1 WAN Module
The WAN Module is a pushable STREAMS module named s_wan. Its purpose is to take an OpenSS7 Communications Device Interface (CDI) Stream and convert it for use as a WAN interface Stream by applications programs, drivers or modules expecting the SpiderX.25 interface. The insertion and use of this module is illustrated in Figure 4.
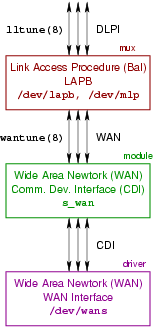
The s_wan pushable STREAMS module accepts a Communications Devce Interface (CDI) at its lower service boundary and provides a Wide Area Network (WAN) Interface at its upper service boundary.
Note that, as s_wan is a pushable module, it is possible to include an
autopush(8) specification a driver providing the Communications Device
Interface (CDI), to provide a specialized device minor or minor device name that
clones Device Layers following the WAN approach.
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stropts.h>
#include <sys/errno.h>
#include <sys/error.h>
#include <sys/snet/wan_proto.h>
#include <sys/snet/wan_control.h>
int fd;
/* Open the communications style device. */
if ((fd = open("/dev/cd", O_RDWR)) < 0) {
perror();
exit(1);
}
/* Push the WAN style module. */
if (ioctl(fd, I_PUSH, "s_wan") < 0) {
perror();
exit(1);
}
/* At this point we can talk to the Stream using
* the service primitives and input-output controls
* of the WAN interface. */
struct wan_tnioc tune;
tune.w_type = WAN_TUNE;
tune.w_snid = snid;
if (ioctl(fd, W_GETTUNE, &tune) < 0) {
perror();
exit(1);
}
B.2 CDI Module
The CDI Module is a pushable STREAMS module named s_cdi. Its purpose is to take a SpiderX.25 WAN interface (WAN) Stream and convert it for use as a Communications Device utilizing the Communications Device Interface (CDI). The insertion and use of this module is illustrated in Figure 5.
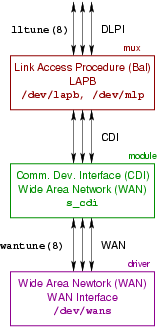
The s_cdi pushable STREAMS module accepts a Wide Area Network (WAN) Interface at its lower service boundary and provides a Communications Devce Interface (CDI) at its upper service boundary.
Note that, as s_cdi is a pushable module, it is possible to include an
autopush(8) specification a driver providing the Wide Area Network
(WAN) Interface, to provide a specialized device minor or minor device name that
clones Device Layers following the CDI approach.
Appendix C WAN Utilities
C.1 WAN Tuning Utility
The WAN Tuning Utility is also documented as a manual page, wantune(8).
Name
wantune – manage WAN tunable parameters
Synopsis
wantune [options] [-G] -s subnet_id [-d devname] [filename]
wantune [options] -P -s subnet_id [-d devname] [filename]
wantune {-h|--help}
wantune {-V|--version}
wantune {-C|--copying}
Description
wantune is a configuration command intended to be executed from system
configuration scripts, and, in particular, the xnetd(8) configuration
daemon. Its purpose is to alter or interrogate the tunable parameters of a WAN
data link connected to an identified subnetwork.
Options
The wantune command accepts the following options:
Command Options
The following command options are mutually exclusive (except for -h, -V and -C which never cause an error when specified with another command option). If no command option is given, -G is assumed.
- -G, --get
- Retrieve configuration information for the specified subnet_id, from the
default or specified device, and write the output to stdout (or
filename, when given). This option can be used to create a properly
formatted configuration file from an existing system configuration.
- -P, --put
- Load configuration information for the specified subnet_id, to the default
or specified device, getting the configuration input from stdin (or
filename, when given). This option can be used to tune current system
configuration.
- -h, --help
- When this option is encountered, usage information is printed to stdout,
option processing stops, and the program exists successfully without taking any
further action.
- -V, --version
- When this option is encountered, version information is printed to
stdout, option processing stops, and the program exits successfully
without taking any further action.
- -C, --copying
- When this option is encountered, copying permissions are printed to stdout, option processing stops, and the program exits successfully without taking any further action.
Non-Command Options
The following non-command options cab be combined together and with any command option. Non-command options that are not necessary for the specified command option do not generate an error by mere combination.
- -e, --extended
- Normally wantune processes a fixed number of lines from stdin
(or filename, when specified), and outputs a fixed number of lines to
stdout (or filename, when specified). This fixed number of lines
are strictly compatible with other implementations of wantune.
When the -e option is specified, additional lines are accepted on input and are generated on output. For the format of the fixed lines and the additional lines, see WAN Tuning File Format.
- -s, --subnet subnet_id
- Specifies the subnetwork identifier, subnet_id, to which the tuning
operation applies. subnet_id is normally an alphabetical character
starting at ‘A’ for the first subnetwork, ‘B’ for the second
subnetwork, and so on. This option must always be given when the -P or
-G options are present or assumed.
- -d, --device devname
- Specifies the device, devname, to open when tuning. When unspecified,
the default is /dev/wans. See also Devices, below.
- -n, --dryrun
- Execute the command (-P or -G) as a dry run. When this option
is specified with the -P option, the input is read and checked for
validity, but the configuration is not written to the device when specified with
the -G option, information is read from the device, but configuration
information is not output. The exit status and diagnostic output of the command
still reflects the success or failure of the command.
- -q, --quiet
- Suppresses normal output. This is the same as ‘--verbose=0’.
- -D, --debug [level]
- Increase or specify the debug verbosity level. The default debug
level is zero (0). This option may be repeated. Level zero (0)
corresponds to no debugging output.
- -v, --verbose [level]
- Increase or specify the output verbosity level. The default output level is one (1). This option may be repeated. Level zero (0) corresponds to no normal output.
Arguments
The following non-option arguments may be provided on the command line:
- filename
- Specifies the filename from which to read (-P option) or write
(-G option) configuration information.
This argument is optional. When the filename is not given and the -P option is specified, the values are read from stdin; for the -G option, values are written to stdout.
If the filename is an absolute path (i.e. begins with ‘/’), then filename is assumed to be the exact path specified. Otherwise, the file required is assumed to be /etc/sysconfig/strx25/template/filename.4 See WAN Tuning File Format, for the format of the file.
Diagnostics
An exit status of zero (0) indicates that the command was successful; one (1) indicates that an error occured and a diagnostic message is printed to stderr; two (2) indicates that the option or argument syntax was in error and a diagnostic message is printed to stderr.
The --quiet option suppresses the printing of normal output to stdout and diagnostic messages to stderr.
File Format
For the input file format, see WAN Tuning File Format.
Notices
On input, this implementation will handle fields that are separated by any whitespace (any number of blanks, horzontal tabs, new lines, carriage returns, vertical tabs, form feeds). On output, newlines are generated after fields.
Devices
- /dev/streams/wans
- /dev/wans
- The Style 2 CDI device for WAN,
wans(4).
Files
- /etc/sysconfig/strx25/template/filename
- The default directory location for configuration files used by this command.5
See Also
Bugs
wantune has no known bugs.
Compatibility
The wantune command is compatible with Spider X.25, and implementations based on Spider X.25, such as AIXlink/X.25, HP-UX, IRIS SX.25, PT X.25, RadiSys WAN, SBE X.25, Solstice X.25, and others, with the following portability considerations:
- A version of this command is provided by OpenSS7 X.25 Networking for
compatibility with systems that require it. Neither this command nor the
xnetd(8)are recommended for configuration of the OpenSS7 X.25 Networking subsystems. Use the SNMP agent instead. - Options -e, -n, -q, -v, -h, -V, -C, and all long options, are specific to this OpenSS7 X.25 Networking implementation of wantune and will not be used by portable command scripts.
- No other implementation documents printing the output to a file when a filename is specified with the -G command option. This is an enhancement of this implementation.
- No other implementation documents the -e, -n, -q, -v, -h, -V, and -C, options. They will not be used by portable command scripts.
- Options --help and --version are provided for compatibility with GNU coding standards (GNITS); --copying, OpenSS7 coding standards.
- wantune attempts to be source (and script) compatible with historical implementations based on Spider X.25, however, binary compatibility is not attempted. Any binary compatibility acheived is likely to be removed in a subsequent release.
For additional compatibilty considerations, see WAN Compatibility and Porting.
Conformance
AIXlink/X.25, HP-UX, IRIS SX.25, PT X.25, RadiSys WAN, SBE X.25, Solstice X.25, documentation. See References.
History
wantune first appeared in Spider X.25.
C.2 WAN Address Mapping Utility
Name
wanmap – manage WAN address mappings
Synopsis
wanmap [options] -D -s subnet -r remote [-d device]
wanmap [options] -G -s subnet -r remote [-d device] [filename]
wanmap [options] -M -s subnet [-d device] [filename]
wanmap [options] -P -s subnet [-d device] [filename]
wanmap [options] -Z -s subnet [-d device] [filename]
wanmap {-h|--help}
wanmap {-V|--version}
wanmap {-C|--copying}
Description
wanmap provides a user space command line program that permits alteration and management of the remote to interface address mapping tables that are associated with a given subnet identifier within the WAN driver. Command options are given to permit the deletion of individual entries, the retrieval of individual entries, the loading of the table from a file for a given subnet, and zeroing of the table for a given subnet.
Options
The wanmap command accepts the following options:
Command Options
The following command options are mutually exclusive: only one command option should be present on the command line at a time. The exceptions are the -h, -V and -C options that can be specified alone, or with any other option.
- -D, --delete
- Deelte the address mapping identified by the remote argument to the
-r option and the subnet argument to the -s option. The
-s and -r options must be specified.
- -G, --get
- Display the address mapping identified by the remote argument to the
-r option and the subnet argument to the -s option. The
-s and -r options must be specified.
- -M, --list
- Display the address mappings identified by the subnet argument to the
-s option. The -s option must be specified.
- -P, --load
- Load the address mappings identified by the subnet argument to the
-s option. The -s option must be specified.
- -Z, --zero
- Delete all address mappings identified by the subnet argument to the
-s option. The -s option must be specified.
- -h, --help
- When this option is encountered, display usage information to stdout,
stop options processing, and exit without taking further action.
- -V, --version
- When this option is encountered, display version information to stdout,
stop options processing, and exit without taking further action.
- -C, --copying
- When this option is encountered, display copying information to stdout, stop options processing, and exit without taking further action.
Non-Command Options
The following common options can be specified together along with a command option. It is not an error to specify options that are not necessary for the command option with which they are specified.
- -r, --remote remote
- Specify the remote address, remote, for which to delete or retrieve an
address mapping. The address mapping is deleted when the -D command
option is given; retrieved for the -G option.
This option must be specified whenever the -D or -G option is
specified.
- -s, --subnet subnet
- Specifies the subnetwork identifier, subnet, to which the command applies.
This option must be specified whenever the -D, -G,
-M, -P or -Z options is specified.
- -d, --device device
- Specify the device name, device, upon which to operate. When this option
is not specified, or device is not given, the default is /dev/wans,
/dev/streams/clone/wans or /dev/streams/wans/0, whichever opens
successfully first.
- -f, --file filename
- Specify the configuraiton file name that holds mapping information to apply to
the device when the -P command option is also specified. When this
option is not specified, or the filename is not given, the default is
/etc/sysconfig/wanmapconf.6
For the format of this file, see WAN Mapping File Format.
- -q, --quiet [level]
- Suppress normal output. Only the return code oof the command is of interest.
This has the same effect as ‘--verbose=0’.
- --debug [level]
- Specify or increase the debugging verbosity level. Sets the debugging
verbosity level, when given, or simply incresases the debug verbosity when
level is not given. This option can be repeated. When level is
specified, only the last repetition takes effect.
- -v, --verbose [level]
- Specify or increase the output verbosity level. Sets the output verbosity level, when given, or simply incresases the output verbosity when level is not given. This option can be repeated. When level is specified, only the last repetition takes effect.
Arguments
The wanmap command takes no non-option arguments.
Diagnostics
An exit status of zero (0) indicates that the command was successful; one (1) indicates that an error occured and a diagnostic message is printed to stderr; two (2) indicates that the option or argument syntax was in error and a diagnostic message is printed to stderr.
The --quiet option suppresses the printing of normal output to stdout and diagnostic messages to stderr.
File Format
For the input file format, see WAN Mapping File Format.
Notices
On input, this implementation will handle fields that are separated by any whitespace (any number of blanks, horzontal tabs, new lines, carriage returns, vertical tabs, form feeds). On output, newlines are generated after fields.
Devices
- /dev/streams/wans
- /dev/wans
- The Style 2 CDI device for WAN,
wans(4).
Files
- /etc/sysconfig/strx25/wanmapconf
- The default directory location for configuration files used by this command.7
See Also
Bugs
wanmap has no known bugs.
Compatibility
wanmap is compatible with Spider X.25, and implementations based on Spider X.25, such as, AIXlink/X.25, HP-UX, IRIS SX.25, PT X.25, RadiSyS WAN, SBE X.25, Solstice X.25, and others, with the following portability considerations:
- Options -q, -v, -h, -V, -C, and all long options, are specified to this OpenSS7 X.25 Networking implementation of wanmap and should not be used by portable command scripts.
- No other implementation documents the -q, -v, -h, -V, and -C, options. They should not be used by portable command scripts.
- Options --help and --version are provided for compatibility with GNU coding standards (GNITS); --coying, OpenSS7 coding standards.
For additiona compatibility information, see WAN Compatibility and Porting.
Conformance
AIXlink/X.25, HP-UX, IRIS SX.25, PT X.25, RadiSyS WAN, SBE X.25, Solstice X.25, documentation.
History
wanmap first appeared in Spider X.25.
Appendix D WAN File Formats
D.1 WAN Mapping File Format
The WAN mapping file format first appeared in Spider X.25.
D.2 WAN Tuning File Format
File Format
The WAN tuning file format corresponds closely to the wan_tnioc
structure. Each line in the file typically corresponds to a member in the
wan_tnioc structure. See wan_tnioc Structure.
The file consists of 12 lines of data as follows:
- WAN_maxframe specifies the maximum frame size for the WAN interface in octets. The value is a positive integer.
- WAN_baud specifies the baud rate for the WAN interface in bits per second. When zero (0), an external clock must be provided. THe value is a positive integer.
- WAN_translate
specifies whether a remote address should be translated into an interface
address using the address mapping function. See
wanmap(8)for more information. When this value is ‘Y’, ‘y’ or ‘1’, the address mapping will be used to translate the remote address. - WAN_phys_int
specifies the physical interface type. This can be the integer numeric value
‘0’, ‘1’ or ‘2’, wehre the interpretation of these values is
described in the table below:
0 WAN_X21X.21 physical interface. 1 WAN_V28V.28 physical interface. 2 WAN_V35V.35 physical interface. - WAN_connect_proc
specifies the calling procedures to be used when generating outgoing calls on
the WAN interface. This can be the values ‘0’, ‘1’, or ‘2’,
where the interpretation of these value is described in the table below:
0 WAN_NONENo calling procedures. 1 WAN_X21PX.21 calling procedures. 2 WAN_V25bisV.25 bis calling procedures. - WAN_x21_T1 specifies the time interval for the X.21 T1 Timer: the amount of time that the DTE will await proceed-to-select having signalled call-request to the DCE. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 30 (3.0 seconds).
- WAN_x21_T2 specifies the time interval for the X.21 T2 Timer: the amount of time that the DTE wil await ready-for-data having signalled end-of-selection. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 200 (20.0 seconds).
- WAN_x21_T3A specifies the time interval for the X.21 T3A Timer: the amount of time that the DTE wil await additional call-progress or DCE-provided-information signals. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 60 (6.0 seconds).
- WAN_x21_T4B specifies the time interval for the X.21 T4B Timer: the amount of time that the DTE wil await ready-for-data having signalled call-accept. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 60 (6.0 seconds).
- WAN_x21_T5 specifies the time interval for the X.21 T5 Timer: the amount of time that the DTE wil await DCE-ready having signalled DTE-clear-request. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 20 (2.0 seconds).
- WAN_x21_T6 specifies the time interval for the X.21 T6 Timer: the amount of time that the DTE wil await DCE-ready having signalled DTE-clear-confirm. The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default value of 20 (2.0 seconds).
- WAN_v25_callreq
specifies the time interval for the V.25 T1 Timer: the amount of time that
the DTE will await successful call establishment afeter having initiated a call.
The value is a short integer number of deciseconds (0.1 seconds), with a default
value of
6000 (600 seconds, or 5 minutes).
Note that V.25 Timer T1 is only necessary when CFI (Call Failure Indication) is not provided by the network.
Appendix E WAN Compatibility and Porting
The typical SpiderX.25 stack implementation is illustrated in Figure 2. This stack profile has the following characteristics:
- The predominant implementation interface at the network layer is the Network Layer Interface (NLI), see NLI.
- The predominant implementation interface at the data link layer is the Data Link Provider Interface (DLPI), see DLPI.
- The predominant implementation interface at the media access or frame layer is the MAC interface for LAN and the WAN interface (for WAN), the later being the subject of this specification.
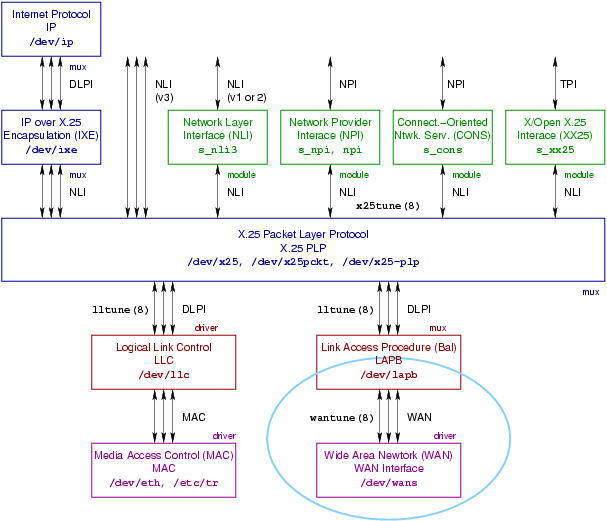
The SpiderX.25 stack implementation differs from the OpenSS7 X.25 Networking one in several fundamental ways:
- OpenSS7 X.25 Networking uses the Network Provider Interface (NPI), see NPI, at the network layer.
- OpenSS7 X.25 Networking uses the Data Link Provider Interface (DLPI), see DLPI, at the data link layer.
- OpenSS7 X.25 Networking uses the Communications Device Interface (CDI), see CDI, at the media access or frame sub-layer.
For the purposes of providing compatibility between the OpenSS7 X.25 Networking implementation approach and the SpiderX.25 implementation approach, OpenSS7 X.25 Networking provides a number of pushable “conversion” modules. See WAN Drivers and Modules.
E.1 Compatibility with AIXlink/X.25
E.2 Compatibility with HP X.25/9000
E.3 Compatibility with IRIS SX.25
E.4 Compatibility with PT X.25
E.5 Compatibility with RadiSys WAN
E.6 Compatibility with SBE X.25
E.7 Compatibility with Solstice X.25
Appendix F Glossary of WAN Terms and Acronyms
| ANSI | American National Standards Institute
|
| CCITT | Old name for ITU-T
|
| CONS | Connection-Oriented Network Service
|
| ENSDU | Expedited Network Service Data Unit
|
| ETSI | European Telecommunications Standards Institute
|
| IEEE | Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
|
| ITU | International Telecommunications Union
|
| ITU-T | ITU Telecom Sector
|
| LCI | Logical Channel Identifier
|
| LLC1 | Logical Link Control Type 1
|
| LLC2 | Logical Link Control Type 2
|
| LLC | Logical Link Control
|
| MAC | Media Access Control
|
| NLI | Network Layer Interface
|
| NPDU | Network Protocol Data Unit
|
| NSAP | Network Service Access Point
|
| NSDU | Network Service Data Unit
|
| NSP | Network Service Provider
|
| NS | Network Service
|
| NSU | Network Service User
|
| PDU | Protocol Data Unit
|
| PVC | Permanent Virtual Circuit
|
| SAP | Service Access Point
|
| SDU | Service Data Unit
|
| VC | Virtual Circuit
|
| X.121 | ITU-T Recommendation X.121
|
| X.25 | ITU-T Recommendation X.25
|
| X.29 | ITU-T Recommendation X.29
|
References
| [AIXlink/X.25] | AIXlink/X.25 Version 2.1
for AIX: Guide and Reference, No: SC23-2520-07, Eighth Edition, September 2006,
(Bolder, CO), International Business Machine Corp., IBM.
IBM Documentation Library.
|
| [ARTIC WAN] | ARTIC STREAMS Support WAN Driver
Interface Reference, Release 1.7, June 2004, (Hillsboro, OR), RadiSys
Corporation, RadiSys. [Doc No: 007-01232-0003], RadiSys Support Documentation.
|
| [CDI] | OpenSS7 CAE Specification: Communications
Device Interface (CDI) Specification, Revision 0.9.2, Draft 2, July 15, 2007,
(Edmonton, Canada), B. Bidulock, OpenSS7 Corporation. Distributed with package
strxns-0.9.2 and openss7-0.9.2.
OpenSS7 Documents.
|
| [DLPI] | Open Group CAE Specification: Data Link
Provider Interface (DLPI) Specification, Revision 2.0.0, Draft 2, August 20,
1992, (Parsippany, New Jersey), UNIX International, Inc., UNIX International
Press. The Open Group,
The OpenSS7 Project.
|
| [IRIS SX.25] | IRIS SX.25 NLI Programmer's
Guide, 1995, (Mountainview, CA), Silicon Graphics, Inc., SGI Technical
Publications. [No: 007-2268-002]. SGI Technical Publications.
|
| [ISO7776] | ISO/IEC 7776:1995, Information
technology – Telecommunications information exchange between systems –
High-level data link control procedures – Description of the X.25
LAPB-compatible DTE data link procedures, Second Edition, July 1, 1995,
International Organization for Standardization.
International Organization for Standardization.
|
| [ISO8802-2] | ANSI/IEEE Standard 802.2-1998
[ISO/IEC 8802-2:1998], IEEE Standard for Information Technology –
Telecommunications and Information Exchange Between Systems – Local and
Metropolitan Area Networks – Specific Requirements – Part 2: Logical Link
Control, May 7, 1998, (New York), ANSI/IEEE, IEEE Computer Society. [ISBN
1-55937-959-6]. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
|
| [ISO8881] | ISO/IEC 8881:1989, Information
Processing Systems – Data Communications – User of the X.25 Packet Level
Protocol in Local Area Networks, 1989, ISO/IEC, International Organization for
Standardization. International Organization for Standardization.
|
| [NLI] | OpenSS7 CAE Specification: Network Layer
Interface (NLI) Specification, Revision 0.9.2, Draft 1, June 2008, (Edmonton,
AB), B. Bidulock, OpenSS7 Corporation. Distributed with package
strx25-0.9.2 and openss7-0.9.2.
The OpenSS7 Project.
|
| [NPI] | Open Group CAE Specification: Network
Provider Interface (NPI) Specification, Revision 2.0.0, Draft 2, August 17,
1992, (Parisppany, New Jersey), UNIX International, Inc., UNIX International
Press. The OpenSS7 Project.
|
| [Solstice X.25] | Solstice X.25 9.2
Administration Guide, October 1999, (Palo Alto, CA), Sun Microsystems, Inc.,
Sun. [Part No: 806-1234-10], Solaris Documentation.
|
| [TPI] | Open Group CAE Specification: Transport
Provider Interface (TPI) Specification, Revision 2.0.0, Draft 2, 1999,
(Berkshire, UK), Open Group, Open Group Publication.
The Open Group,
The OpenSS7 Project.
|
| [V.25 bis] | ITU-T Recommendation V.25 bis (10/96),
Synchronous and asyncrhonous automatic dialing procedrues on switched
networks, October 1996, (Geneva), ITU, ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization
Sector of ITU, (Previously “CCITT Recommendation”),
http://www.itu.int/rec/T-REC-V.25bis/en/ T-REC-V.25bis.
|
| [X.21] | ITU-T Recommendation X.21 (09/92),
Interface between Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) and Data
Circuit-terminating Equiment (DCE) for synchronous operation on Public Data
Networks, September 1992, (Geneva), ITU, ITU-T Telecommunication
Standardization Sector of ITU. (Previously “CCITT Recommendation”),
T-REC-X.21.
|
| [X.21 bis] | ITU-T Recommendation X.21 bis (03/88),
Use on Public Data Networks of Data Terminal Equipment (DTE) which is
designed for interfacing to synchronous V-series modems, March 1988, (Geneva),
ITU, ITU-T Telecommunication Standardization Sector of ITU. (Previously “CCITT
Recommendation”), T-REC-X.21bis.
|
| [X.25] | ITU-T Recommendation X.25.
T-REC-X.25.
|
| [X.29] | ITU-T Recommendation X.29.
T-REC-X.29.
|
| [XX25] | X/Open CAE Specification: X.25 Programming
Interface using XTI (XX25), No. c411, November 1995, (Berkshire, UK), X/Open,
Open Group Publication. [ISBN: 1-85912-136-5].
The Open Group.
|
Index
autopush(8): CDI Moduleautopush(8): WAN ModuleCD_ATTACH_REQ(7): WAN_SID - Set Subnetwork IdentifierCD_DISABLE_CON(7): WAN_CTL - ControlCD_DISABLE_REQ(7): WAN_CTL - ControlCD_ENABLE_CON(7): WAN_CTL - ControlCD_ENABLE_REQ(7): WAN_CTL - ControlCD_ERROR_IND(7): WAN_NTY - NotifyCD_ERROR_IND(7): WAN_CTL - ControlCD_MODEM_SIG_IND(7): WAN_NTY - NotifyCD_MODEM_SIG_POLL(7): W_GETSIG - Get Signals and LeadsCD_MODEM_SIG_POLL(7): WAN_NTY - NotifyCD_MODEM_SIG_REQ(7): W_SETSIG - Set Signals and LeadsCD_UNITDATA_IND(7): WAN_DAT - DataCD_UNITDATA_REQ(7): WAN_DAT - Datacdi(7): W_GETSIG - Get Signals and Leadscdi(7): W_SETSIG - Set Signals and Leadscdi(7): WAN_NTY - Notifycdi(7): WAN_DAT - Datacdi(7): WAN_CTL - Controlcdi(7): WAN_SID - Set Subnetwork Identifierdpkg(1): Footnotesdpkg(1): Footnotesdpkg(1): Footnotesdpkg(1): Footnotesfilename: WAN Tuning Utilitygetmsg(2s): Footnotesgetpmsg(2): Footnotesioctl(2): W_GETSIG - Get Signals and Leadsioctl(2): W_SETSIG - Set Signals and Leadsioctl(2): W_DISABLE - Disable Interface Data Transferioctl(2): W_ENABLE - Enable Interface Data Transferioctl(2): W_STATUS - Get Interface Statusioctl(2): W_DELWANMAP - Delete WAN Address Mappingsioctl(2): W_GETWANMAP - Get WAN Address Mappingioctl(2): W_PUTWANMAP - Put WAN Address Mappingioctl(2): W_GETTUNE - Get Tunablesioctl(2): W_SETTUNE - Set Tunablesioctl(2): W_GETSTATS - Get Statisticsioctl(2): W_ZEROSTATS - Zero Statisticsputmsg(2s): Footnotesputpmsg(2): Footnotesrpm(1): Footnotesrpm(1): Footnotesrpm(1): Footnotesrpm(1): Footnotesstreamio(7): W_GETSIG - Get Signals and Leadsstreamio(7): W_SETSIG - Set Signals and Leadsstreamio(7): W_DISABLE - Disable Interface Data Transferstreamio(7): W_ENABLE - Enable Interface Data Transferstreamio(7): W_STATUS - Get Interface Statusstreamio(7): W_DELWANMAP - Delete WAN Address Mappingsstreamio(7): W_GETWANMAP - Get WAN Address Mappingstreamio(7): W_PUTWANMAP - Put WAN Address Mappingstreamio(7): W_GETTUNE - Get Tunablesstreamio(7): W_SETTUNE - Set Tunablesstreamio(7): W_GETSTATS - Get Statisticsstreamio(7): W_ZEROSTATS - Zero Statisticswanmap(8): WAN Tuning File Formatwans(4): WAN Address Mapping Utilitywans(4): WAN Tuning Utilitywantune(8): WAN Tuning Utilityxnetd(8): WAN Tuning Utility
Short Contents
- Wide Area Network Interface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Model of the WAN Layer
- 3 WAN Services
- 4 WAN Message Primitives
- 5 WAN Input-Output Controls
- Appendix A WAN Header Files
- Appendix B WAN Drivers and Modules
- Appendix C WAN Utilities
- Appendix D WAN File Formats
- Appendix E WAN Compatibility and Porting
- Appendix F Glossary of WAN Terms and Acronyms
- References
- Index
Table of Contents
- Wide Area Network Interface
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Model of the WAN Layer
- 3 WAN Services
- 4 WAN Message Primitives
- 5 WAN Input-Output Controls
- 5.1 Input-Output Control Data Structures
- 5.2 Input-Output Control Commands
- 5.2.1 W_ZEROSTATS - Zero Statistics
- 5.2.2 W_GETSTATS - Get Statistics
- 5.2.3 W_SETTUNE - Set Tunables
- 5.2.4 W_GETTUNE - Get Tunables
- 5.2.5 W_PUTWANMAP - Put WAN Address Mapping
- 5.2.6 W_GETWANMAP - Get WAN Address Mapping
- 5.2.7 W_DELWANMAP - Delete WAN Address Mappings
- 5.2.8 W_STATUS - Get Interface Status
- 5.2.9 W_ENABLE - Enable Interface Data Transfer
- 5.2.10 W_DISABLE - Disable Interface Data Transfer
- 5.2.11 W_SETSIG - Set Signals and Leads
- 5.2.12 W_GETSIG - Get Signals and Leads
- Appendix A WAN Header Files
- Appendix B WAN Drivers and Modules
- Appendix C WAN Utilities
- Appendix D WAN File Formats
- Appendix E WAN Compatibility and Porting
- Appendix F Glossary of WAN Terms and Acronyms
- References
- Index
Footnotes
[1] See getmsg(2s), getpmsg(2),
putmsg(2s) and putpmsg(2) manual pages.
[2] See W_DISABLE - Disable Interface Data Transfer.
[4] Note
that the precise location of the /etc/sysconfig directory varies
depending upon whether the build was on a dpkg(1)-based or
rpm(1)-based system.
[5] Note that the precise location of the
/etc/sysconfig directory varies depending upon whether the build was
on a dpkg(1)-based or rpm(1)-based system.
[6] Note that the precise location of
the /etc/sysconfig directory varies depending upon whether the build
was on a dpkg(1)-based or rpm(1)-based system.
[7] Note that the precise location of the
/etc/sysconfig directory varies depending upon whether the build was
on a dpkg(1)-based or rpm(1)-based system.
SS7 for the
Common Man
| Home |
© Copyright 1997-2007 OpenSS7 Corporation All Rights Reserved.